The eroding and weathering coastline can pose many challenges to society, such as loss of homes, loss of habitat and loss of income.
What is coastal flooding?
Coastal flooding is flooding that occurs when land that is usually dry is flooded with seawater, often low-lying areas. The primary causes of coastal flooding are:-
- The height of land above sea level – the lower the land, the more endangered a site is. Rising sea levels are challenging the height of the land.
- The intensity of erosion and subsidence – the more intense the erosion or subsidence (sinking land), the more at risk of flooding.
- Lack of natural barriers, like dunes, mangrove forests and vegetation removal – these act as barriers for the waves and reduce their power when they reach land.
- Storm surges – these are temporary rising of sea levels, caused by tsunamis or cyclones, which exceed normal tidal levels.
What is coastal management?
There are a few management strategies that can be employed to ‘save’ the coastline from the effects – there is hard engineering which is when you attempt to control natural processes, and soft engineering tends to accommodate more natural and sustainable methods, working with natural processes. Both methods have pros and cons, and you have likely seen many examples of both types without even realising it.
Hard Engineering Strategies
Sea Walls
Sea walls are large, often concreate walls, that are placed at the vulnerable area, usually the base of a cliff to prevent erosion. They attempt to take the energy of the sea’s force and reflect it back, bearing the brunt of the erosion instead of the cliff base.
Advantages
- They have proven effective at protecting lane
- They can be used by the public to walk or fish along them
- They are not always unsightly
Disadvantages
- Waves can remain powerful and cause damage to wall that must be maintained
- They are expensive to create and maintain
- Can prove unpopular as they may change the aesthetic of the land – large, concrete plinths
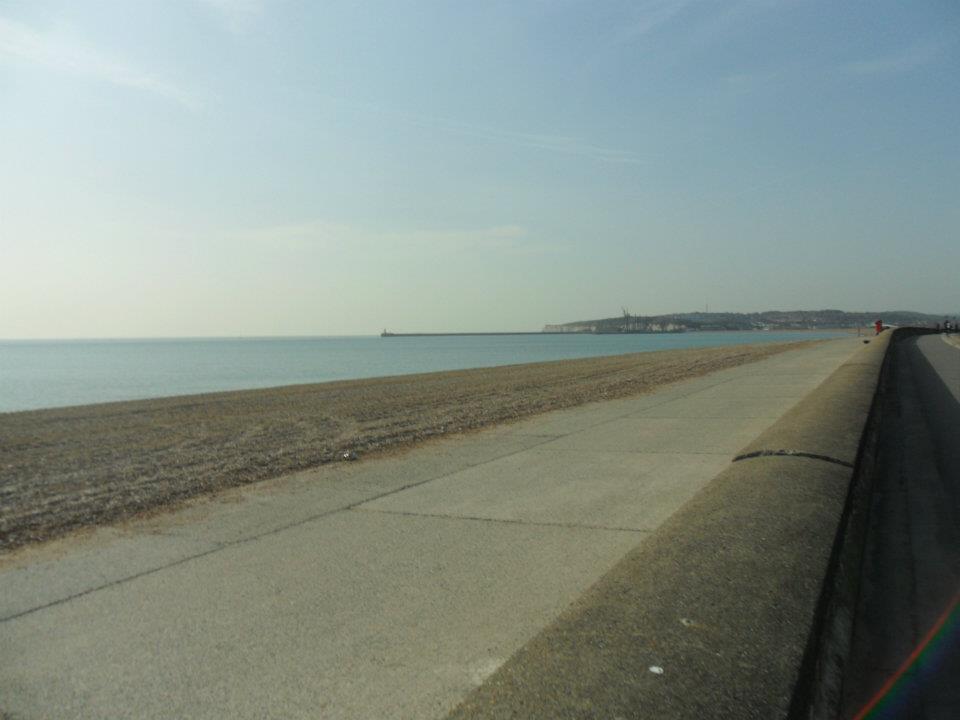


Rock Armour (Rip-Rap)
Rock Armour or ‘Rip-Rap’ is large boulders placed in the vulnerable area to protect it from erosion. Like walls, they are often placed at the base of a cliff to absorb energy and bear the brunt of erosion.
Advantages
- Cheaper than a sea wall to create and maintain
- Easier to maintain as they are not uniform and already have crevices
- Can be used for fishing, though not appropriate for walking
Disadvantages
- They look different to the local geology and site as often rocks are imported
- They can look unsightly, large, jagged boulders and are not safe to climb.
- The rocks are expensive to transport.


Gabions
Gabions are much like rock armour, but they are placed in cages and surround he vulnerable area. Like rock armour, they are placed at the vulnerable area to face the erosion instead of the coastline.
Advantages
- They are cheap and effective at combating some erosion
- They absorbs the wave energy and protect the coastline
- They are less obvious than other defences
Disadvantages
- They are not as strong as other defences
- Like rock armour, they look unnatural
- Items may get trapped in the cages
Groynes
Groynes are wooden or rock structures built at right-angles extending into the sea. They aim to combat the effects of long-shore drift by trapping sediment and making it slower to move. The more sediment and material trapped, the better rate of protecting the coastline.
Advantages
- Trapping sediment builds a beach
- Beach generation can encourage tourism and help local economies
Disadvantages
- It can increase erosion elsewhere by trapping sediment
- They can look unattractive
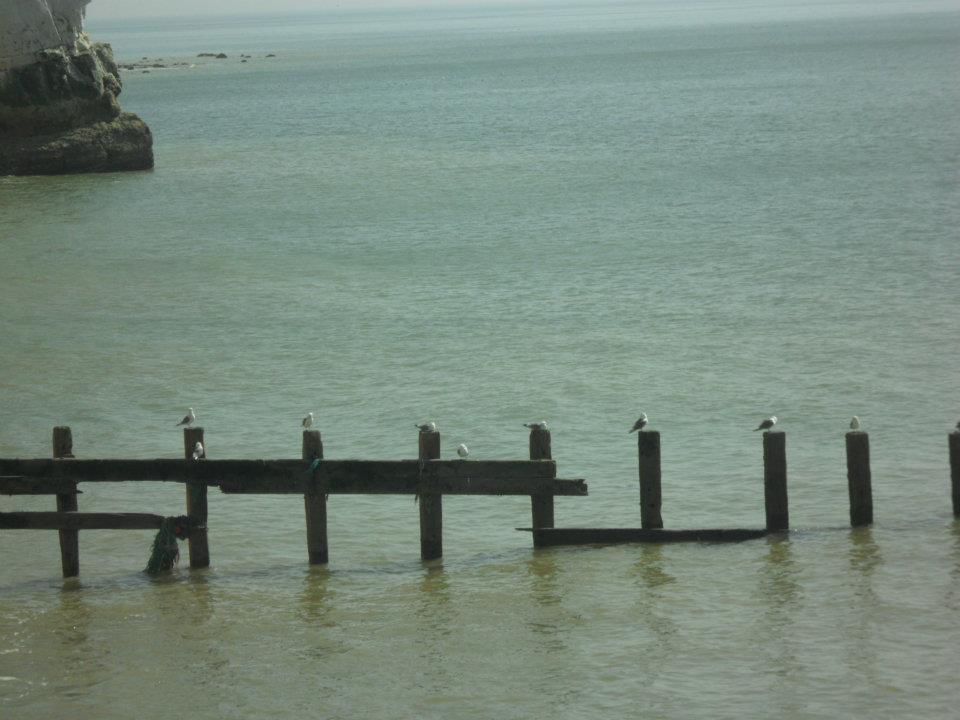
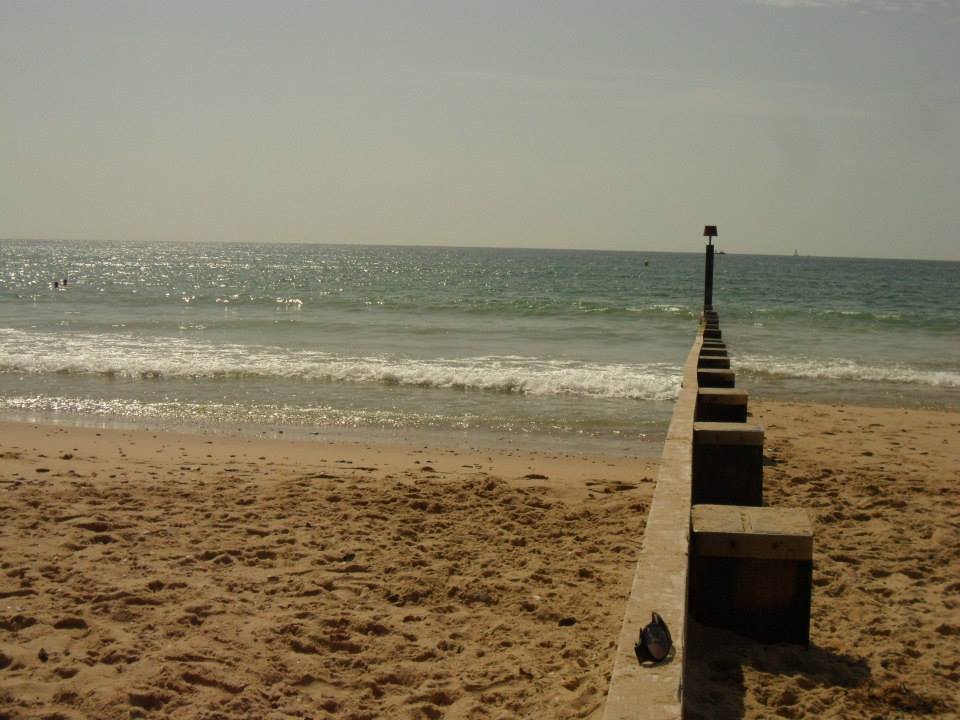


Soft Engineering Strategies
Beach Nourishment
Beach Nourishment is simply the replenishment of beaches, and comprises of adding sand to the beach to maintain sediment levels.
Advantages
- It blends in with the existing beach and can be aesthetically pleasing
- It creates larger beaches which can appeal to tourists and help the local economy
- More popular and seen as natural
Disadvantages
- Sand needs to be constantly replaced
- The sand has to be brought in from elsewhere, which can be expensive
- It doesn’t seem to tackle the problem of eroding cliffs


Beach Reprofiling
Reprofiling a beach is redistributing sediment from the lower part of the beach to upper parts. This would create a more even erosion rate and offer protection to that near the upper beach.
Advantages
- It is a cheap and simple method
- It can reduce the energy of the waves
- The area remains natural looking and more fitting for the local area
Disadvantages
- This method only works when wave energy is low
- You need to repeatedly reprofile the beach
- You need enough sediment to re-distribute
Dune Nourishment
Dunes can help trap sediment and help re-build beaches. Marram grass and other dune plants can be planted to stabilise the dunes and help trap sediment.
Advantages
- It can be a cheap option
- Dune management can keep a natural-looking coastline.
Disadvantages
- Can be easily damaged by storms
- Arears may have to be protected from the public, which isn’t always popular
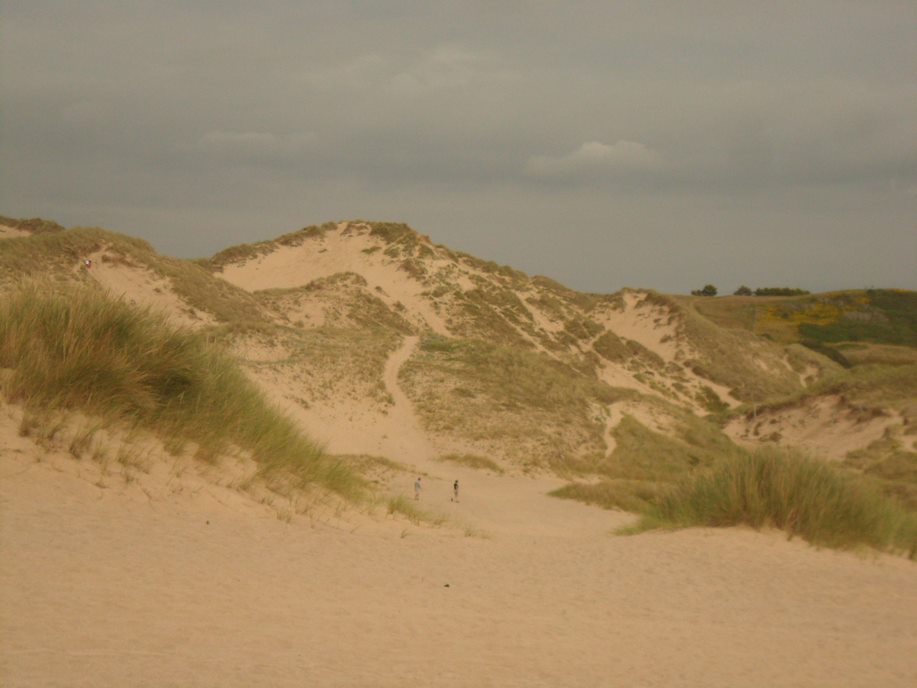
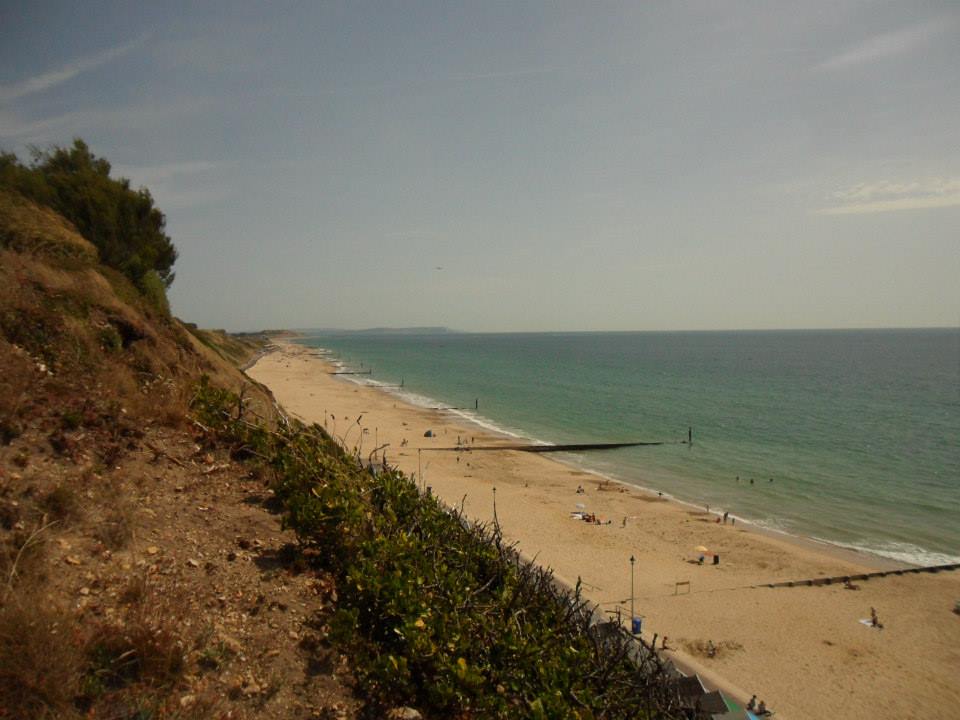


Managed Retreat
Managed retreat, or coastal re-alignment, is the controlled flooding of low-lying coastal areas, allowing them to flood and be lost to the sea overtime. Areas of high-risk erosion can be ‘let-go’ as engineering may be too costly or ineffective. This can be regarded as an option if the land can be lost, like low-value farmland, as opposed to large towns and cities.
Advantages
- Can be a cheaper option compared to engineering.
- Can form a natural defence against erosion and flooding
- Can create habitats or ecosystems for various species
Disadvantages
- Land is lost as it is reclaimed by the sea.
- Some land may be regarded as valuable by locals or property owners
- Compensation for landowners and property owners, which can be costly
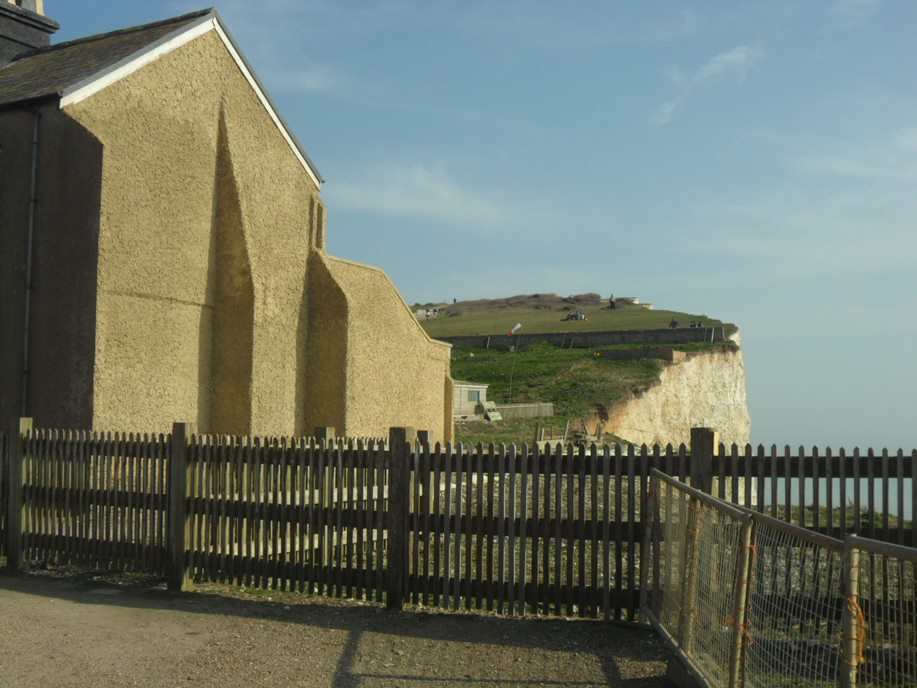
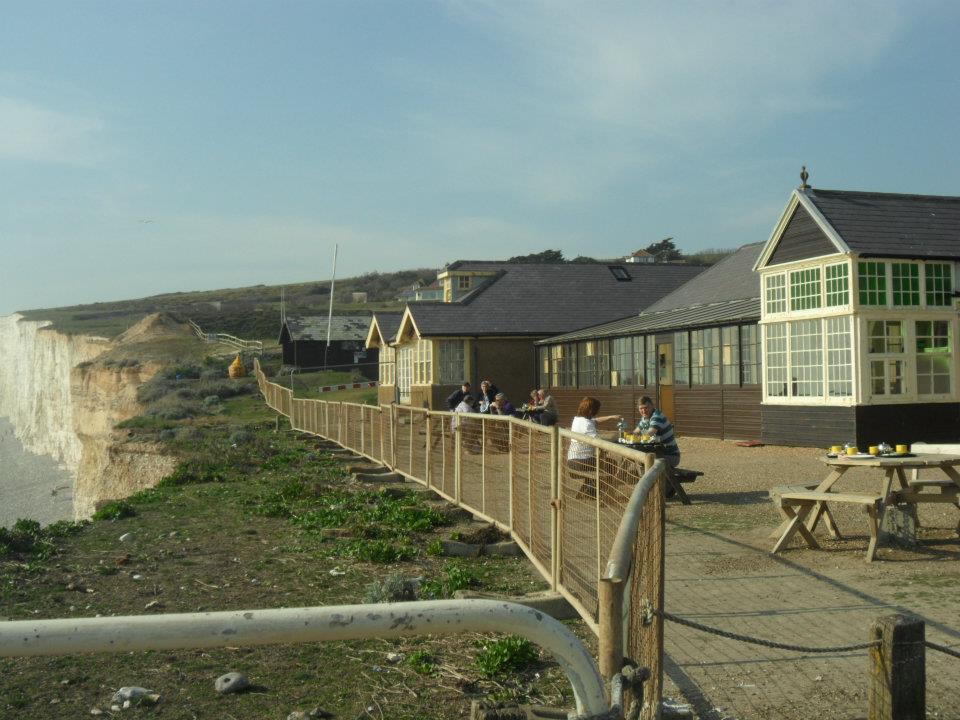


Why Manage Coastlines?
Coastlines can provide vital living space for humans and habitat for species. Many people live by the coast, and endangerment to this could result in mass-migration of people escaping their homes due to the threat. There are many businesses and industries that are located by the coast, and failure to protect the coastline could severely impact the society and economy, such as tourism, not just locally but nationally as well.
Have you been to a beach or cliff before? Perhaps you have surfed or swam in the sea, or even climbed a cliff or participated in coasteering. Think of what you enjoyed about the coast and why people might live in these vulnerable locations.
Climate Change can cause further impacts on populations by the coastline, as storm surges and unpredictable weather events, coupled with rising sea levels, are likely to endanger more lives. Therefore, it is of paramount importance for nations to protect their coastlines, and also preserve international coastlines too due to the wider impacts.
Coastal flooding and rising sea level endangers a considerable amount of people in the world. Think of low lying islands which are going to be impacted, such as the Netherlands and Pakistan.